Docs
Platforms In Depth - Kubernetes
In depth look at the Kubernetes platforms
The Kubernetes platform delivers a complete Kubernetes container orchestration cluster, incorporating tools for monitoring, ingress control, and application management. It empowers you to run Kubernetes applications seamlessly within Azimuth or implement custom installations using Helm Charts or Kustomize to oversee Kubernetes manifests. Once your platform is up and running, you’ll find a kubeconfig file in the platform Details section, ready for use with helm or kubectl.
To configure your cluster, you’ll need to provide a unique name and select a cluster template, which determines the Kubernetes version.
Every cluster needs at least one node group of worker nodes. Give each node group a unique name and choose the appropriate cloud instance size based on your needs, considering factors like CPU, RAM, and GPUs. You can enable autoscaling to allow the node group to adjust its size automatically, or you can set a fixed number of instances. If you enable autoscaling, you’ll need to define the minimum and maximum number of instances.
By default, all cluster addons are enabled. These include the Kubernetes dashboard, cluster monitoring with Grafana, and an applications dashboard for easy installation. All dashboards can be accessed from the platforms page.
The advanced options are pre-set with reasonable defaults. Proceed cautiously when modifying these, as incorrect configurations could lead to issues, including deployment failures.
Some configuration options include:
- autohealing: enable this to let the cluster automatically attempt to fix unhealthy nodes
- Kubernetes Ingress: enable this to use Kubernetes Ingress to expose services in your cluster via a load balancer (you’ll need an external IP available in your project for the load balancer). Do not use this option and deploy your own ingress.
- cert-manager: enable this to use
cert-managerto manage TLS certificates for your cluster services.
Platform creation
To create a Kubernetes cluster, navigate to the project/tenancy landing page, click New platform and select Kubernetes from the Create a new platform window.
Enter the cluster name, select a cluster template to use, select a control plane to use, select or add a new node group, enable or disable cluster addons, enable Kubernetes dashboard and enable cluster monitoring.
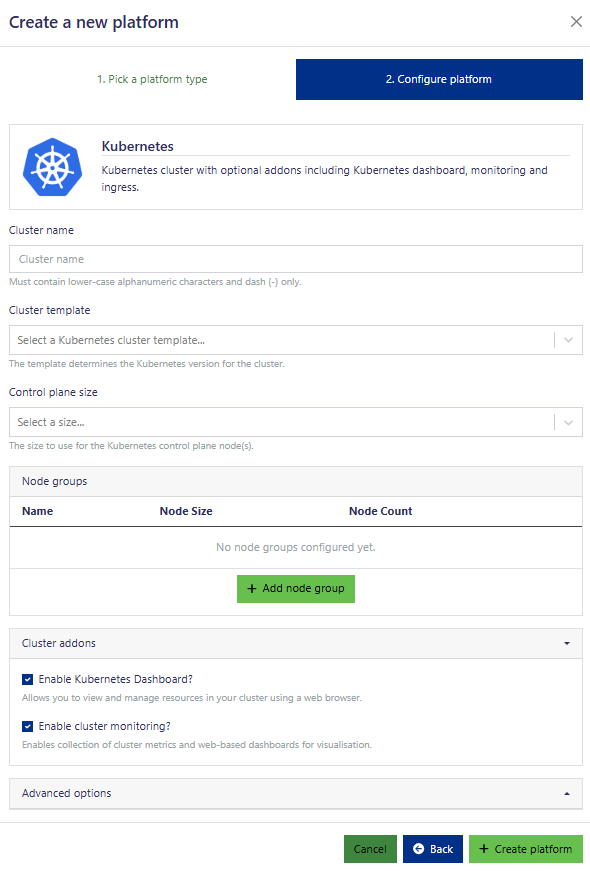
In order to create a Kubernetes platform, we also have to define a node group for the Kubernetes worker nodes.
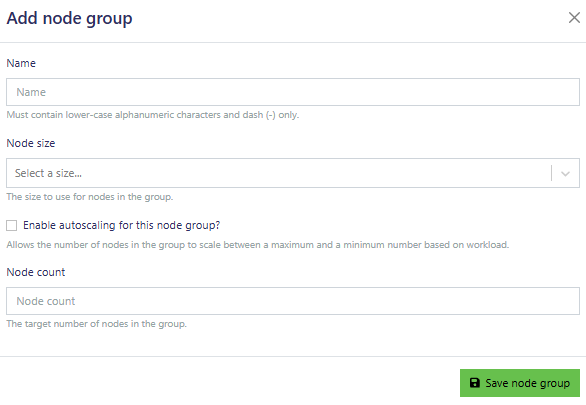
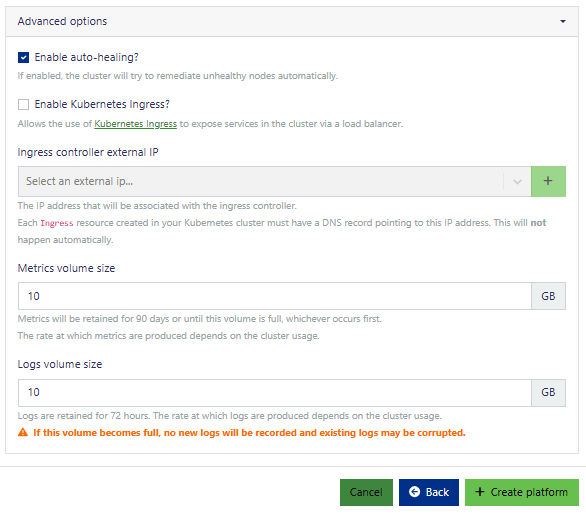
Click create platform to proceed.
From the Platform scheduling window, confirm the options selected in the previous section and once the deployment is complete, the cluster becomes available from the Azimuth landing page for the tenancy.
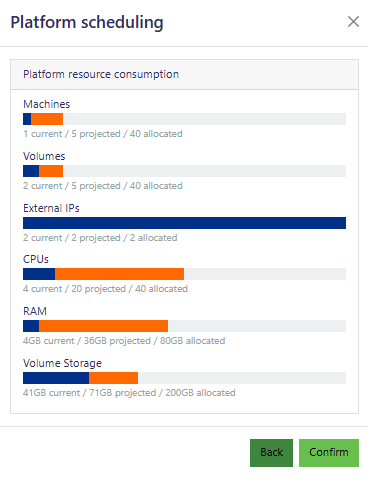
Platform Usage
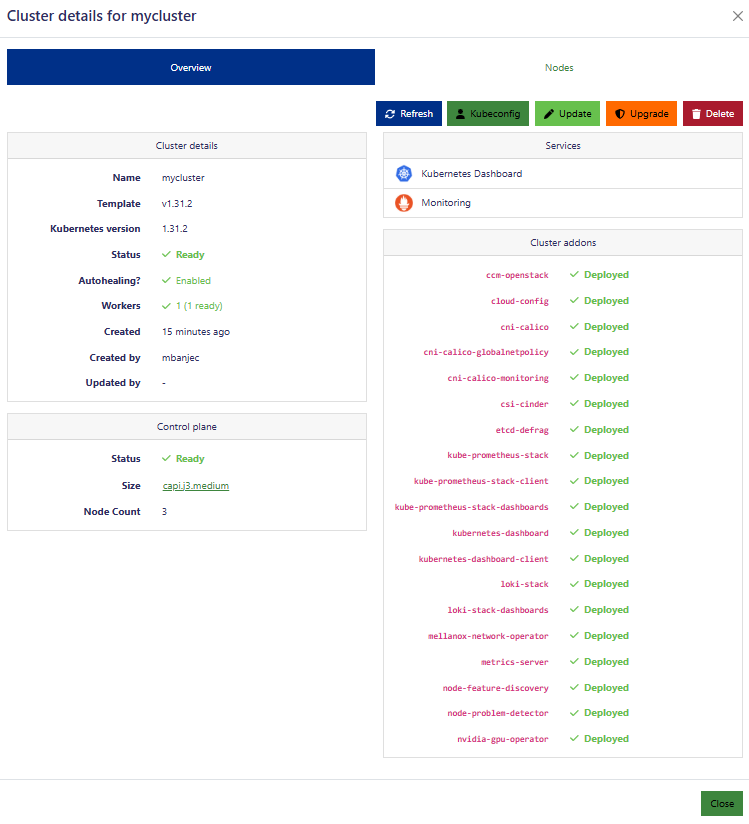
From the Cluster details windows you can: view the Kubeconfig file (for interacting with the cluster from your local computer), Update the configuration of the cluster, Upgrade the images used for patching or upgrading the Kubernetes version, and Delete the cluster. The installed Cluster addons are shown in the right panel. The Nodes tab shows information on the nodes in the cluster.
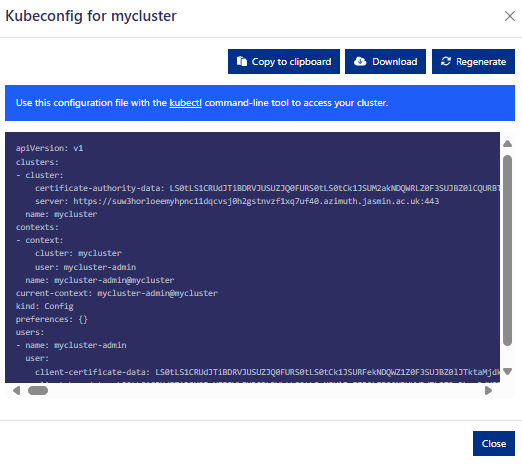
Click Kubeconfig. You can then copy or download the kubeconfig file for accessing the cluster using kubectl from your local computer.
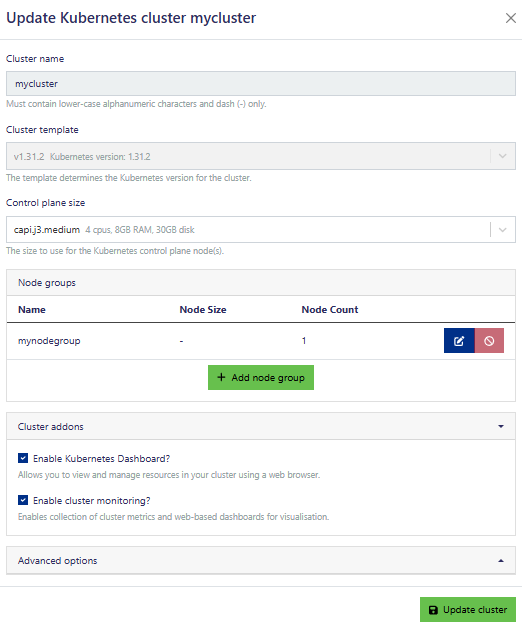
Available Update options include: the ability to change to a different control plane size, adding or removing node group(s), enabling/disabling: Kubernetes Dashboard, cluster monitoring, enable auto-healing, enable Kubernetes Ingress, change the Metrics and logs volumes. You can change the cluster size by defining the node size and count from the node group, either editing the existing node group, or creating a new one (node groups can be different sizes with different numbers of machines).
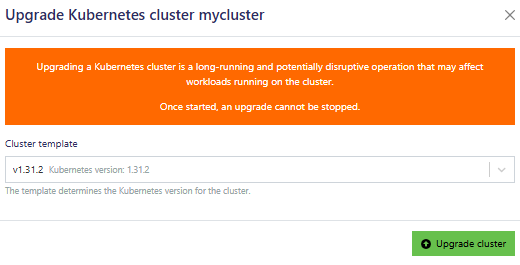
Additionally you can Upgrade the images in the cluster and potentially the Kubernetes version to a newer one. Note that the version of Kubernetes can not be downgraded. If you need to go back to an earlier version of Kubernetes, you would need to create a new cluster.
You can also permanently Delete the cluster.
The Kubernetes Dashboard provides an alternative option to managing the cluster as opposed to downloading the kubeconfig file.
Monitoring the Kubernetes instance is provided by a Grafana dashboard.
For links to resources for Kubernetes, see the Best Practice section.