Docs
Platforms In Depth - JupyterHub, DaskHub, BinderHub
In depth look at the JupyterHub platforms
JupyterHub
JupyterHub is a multi-user platform that allows multiple users to access and run Jupyter notebooks through a web interface. It is designed to provide a standardised computing environment for groups, such as classes or research teams, by launching individual Jupyter notebook instances for each user. The primary purpose of JupyterHub is to facilitate collaborative and scalable data science and research. It allows users access to a consistent computing environment from any device with a web browser where they can share resources efficiently within a team or class. Administrators can manage user authentication and resource allocation centrally.
To create a JupyterHub instance on Azimuth, you will need an existing Kubernetes cluster.
Platform creation
To create a JupyterHub Platform navigate to Azimuth Project/Tenancy page and click on New platform. Then select JupyterHub platform from the Create a new platform page.
Enter the Platform name and either select an existing Kubernetes cluster or create one here by clicking the plus sign at the end of the textbox. Enter the cluster details: Name | Template | Version | number of worker nodes and define auto healing if needed and deploy the instance creation.
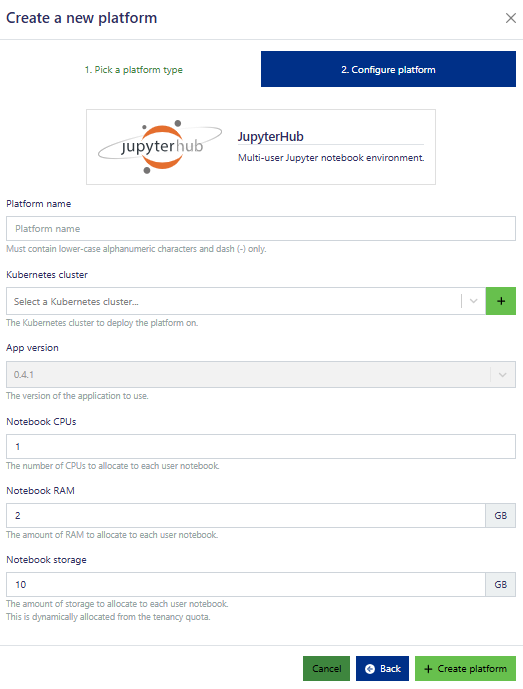
Once successfully deployed, you can access the platform from the Azimuth tenancy landing page.
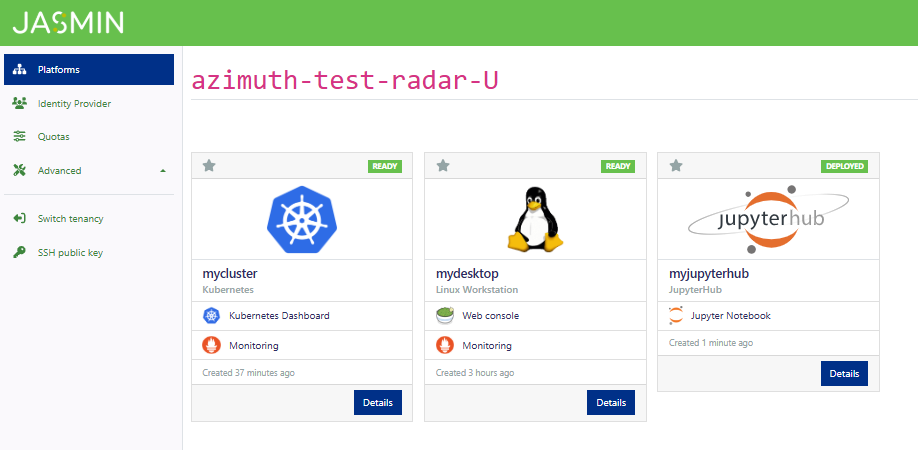
From the platform details page you can access the jupyter notebook service from the services section. Use the details button for the deployed JupyterHub instance to refresh, update, or delete the service.
To update the JupyterHub instance, use the update window to change the Notebook CPUs, Notebook RAM, and Notebook storage.
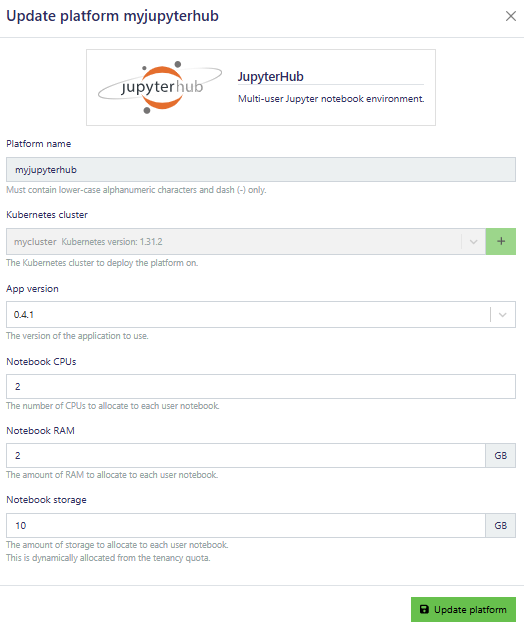
Click update platform to make the changes take effect.
Patching a JupyterHub instance involves updating the software to fix bugs or vulnerabilities, which can typically be done by accessing the Kubernetes Cluster, from the Kubernetes dashboard, or through command-line tools. You can apply updates to the JupyterHub deployment using Kubernetes commands or from the Applications dashboard. To ensure that the updated version is running, you can restart the JupyterHub service.
Azimuth offers several Jupyter-based options such as:
- JupyterHub, as mentioned above
- Jupyter Notebook, a single-user notebook service that can be launched from a
repo2docker-compatible repository, similar to Binder2 - JupyterLab, an enhanced interface for Jupyter notebooks, providing additional features like code consoles, terminals, and a file browser.
Platform usage
To access the deployed JupyterHub instance, click Juptyer Notebook on the platform tile. This link can be shared with others to access the same JupyterHub instance. If the user accessing it is logged into Azimuth, then they will be logged in to JupyterHub using their Azimuth user. For others who don’t have access to Azimuth, users will need to be created using the tenancy’s Identity Provider by the tenancy admin, the details of which then need to be shared with the users who need access.
DaskHub
DaskHub is a cloud-based platform designed to simplify and accelerate distributed data processing tasks using Dask. It provides a user-friendly interface that abstracts away the complexities of setting up and managing Dask clusters, allowing users to focus on their data analysis and machine learning workflows.
Key features and benefits include:
- simplified cluster management handles the provisioning, scaling, and management of Dask clusters, eliminating the need for users to manually configure and maintain infrastructure
- scalability allows platform users to scale Dask clusters up or down to accommodate varying workloads, ensuring optimal resource utilisation and performance.
Additionally, Dask offers a user-friendly web interface that is intuitive and easy to use, even for users who are not familiar with Dask or distributed computing. Dask also integrates seamlessly with popular data science tools like JupyterLab, allowing users to build on their existing workflows and libraries. Azimuth DaskHub comes pre-installed with a wide range of popular libraries and packages, including NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn, and TensorFlow, making it easy to get started with data analysis and machine learning tasks.
In much the same way as JupyterHub, to use Dask, you need to first create a Dask cluster with the desired number of workers and memory allocation. Once the cluster is created, data can be uploaded to the platform or accessed from external storage sources. A user can then start to submit Dask tasks and workflows to the cluster, which are executed in parallel across the worker nodes. The platform provides tools to monitor cluster health, task progress, and resource usage. Additionally, users can also manage their clusters, such as scaling them up or down as needed.
Azimuth DaskHub can be used to perform large-scale data analysis and visualization tasks, such as exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, and data cleaning. Additionally, the platform is well-suited for training and deploying machine learning models on large datasets, including tasks like image classification, natural language processing, and recommendation systems. Azimuth DaskHub can also be used for various scientific computing tasks, such as simulations, numerical modeling, and data processing.
BinderHub
Another platform is Azimuth BinderHub, a cloud-based platform that provides a convenient way to create and share interactive computing environments based on Jupyter Notebooks. It uses Project Jupyter’s Binder technology to dynamically generate Jupyter environments from GitHub repositories, making it easy for users to explore, analyze, and collaborate on data science projects.
Azimuth BinderHub allows users to create and share interactive Jupyter Notebooks, which are a powerful tool for data analysis, visualization, and machine learning. Additionally, the platform integrates seamlessly with GitHub, making it easy to create Binder environments from public or private repositories. Users can simply provide a GitHub repository URL, and Azimuth BinderHub will automatically build the corresponding Jupyter environment. Azimuth BinderHub provides a high degree of customization for Jupyter environments. Users can specify the desired Python version, libraries, and other dependencies in their GitHub repository, ensuring that the environment is tailored to their specific needs. Azimuth BinderHub facilitates collaboration among data scientists and researchers. Users can share their Binder environments with colleagues, allowing them to explore and interact with the same data and code.
The platform helps to ensure reproducibility in data science workflows, by sharing Binder environments where users can provide others with a self-contained environment that can be used to replicate their results. Azimuth BinderHub is accessible from any device with an internet connection, making it a convenient tool for users who need to work on data science projects remotely. Users create a GitHub repository containing the necessary files for their Jupyter environment, including Jupyter Notebooks, Python scripts, and configuration files.
Binder Build: When a user accesses a GitHub repository through Azimuth BinderHub, the platform triggers a Binder build process. This process creates a Docker image based on the specified dependencies and configuration.
Interactive Environment: Once the Docker image is built, Azimuth BinderHub launches an interactive Jupyter environment that can be accessed through a web browser. This environment contains all of the files and dependencies defined in the GitHub repository.