Docs
LOTUS overview
Overview of the LOTUS batch computing cluster, part of JASMIN
What is LOTUS
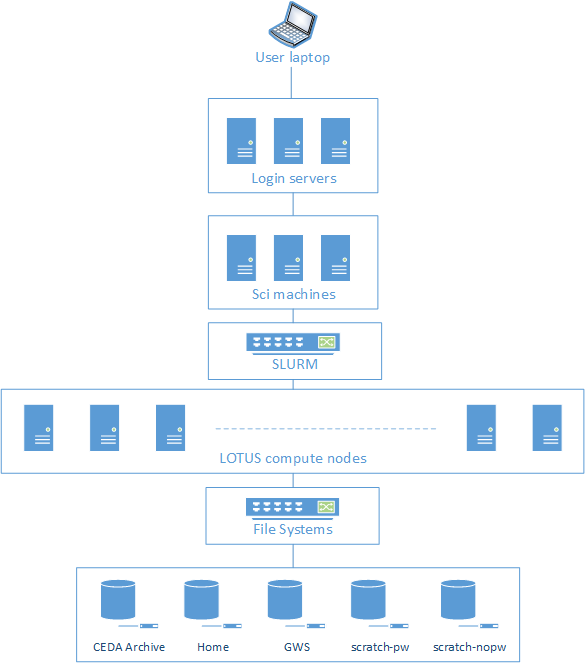
LOTUS is not, in itself, a High-Performance Computing (HPC) facility, but provides the batch and parallel processing component of the JASMIN data- intensive scientific analysis environment. LOTUS is a cluster of physical machines, running the Slurm workload manager, enabling efficient scheduling of larger data analysis tasks across nodes in the cluster as a single unit - see Figure 1.
Each node in the cluster is connected by 10Gbit/s Ethernet to JASMIN’s high-performance 40Gbit/s core network. Although not its primary function, LOTUS also facilitates MPI-based parallel processing.
JASMIN provides both interactive and batch computing environments, recognising that scientists often need to develop and test workflows interactively before running those workflows efficiently at scale. Nodes within LOTUS run the same stack of software and can access the same high-performance storage as the JASMIN scientific analysis servers, ensuring a consistent working environment for all phases of users’ workflows.
See LOTUS Hardware for details of the current LOTUS environment summarised in this schematic presentation.
Figure 1 shows a schematic presentation of the LOTUS cluster and its environment
When to use LOTUS
LOTUS is ideally suited to workflows which need to process or compare entire
datasets, stored either in Group Workspaces or in the CEDA archives. The
latter are directly accessible read-only so can be processed in-place without
the need to copy files. Intermediate working files (within batch jobs) should
be stored temporarily in /work/scratch-pw* and /work/scratch-nopw*
volumes which are shared across the cluster, while persistent outputs can be
written efficiently to Group Workspaces and shared with collaborators for the
duration of a project.
See Access to Storage for details about which file systems are appropriate to use and how to access them.
LOTUS currently has over 53,000 cores*, but is heavily used and implements a fair-share scheduling system between users. It is not intended as a substitute for dedicated HPC facilities, rather as a complementary environment in which model outputs can be analyzed and compared with observational data. Users with large-scale compute-heavy requirements (in particular those requiring large-scale parallel processing) should look to access other parts of the national HPC infrastructure such as ARCHER2 or MONSooN .
*The exact number of cores available varies for operational reasons.
In order to maintain a safe and reliable working environment for all within LOTUS and more widely within JASMIN, users are expected to follow the best practice outlined in this documentation.
How to gain access to LOTUS
LOTUS is accessible via the Slurm batch scheduler that is available to use from all JASMIN scientific analysis servers.
From the above servers, it is possible to submit, monitor, and control batch jobs using the Slurm commands.
For more details about how to use LOTUS, please see our article about how to submit a job to Slurm.